Cucurbit Genetics Cooperative Report 22:31-33 (article 12) 1999
Young-Seok Kwon
National Alpine Agricultural Experiment Station, Pyongchang, Korea.232-950
Fenny Dane
Department of Horticulture, Auburn University, AL 36849 USA
Introduction
Watermelon, Citrullus lanatus (Thunb,) is cultivated in many countries of the world. It is an important vegetable crop in Korea, where the acreage in 1998 was more than 35,000 ha. Although there have been many inheritance studies of watermelon mutants, watermelons have received relatively little genetic attention compared to other crops. Studies of the inheritance and linkages of various characteristics may give valuable information for the breeding of cultivated watermelon.
Many studies have been conducted to investigate the inheritance of morphological characteristics in watermelon (7). Yellow leaf, for example, was reported to be incompletely dominant to green leaf (6), while the andromonoecious character was found to be recessive to monoecious (2,4). Flower petal color is commonly yellow, but light green flowers were detected in watermelon accession kw695. This study was undertaken to determine the mode of inheritance of light green (petal) flower color.
Methods
The watermelon parent material used in this study, Kw-695 and Dalgona, was obtained from the Gene Bank of Rural Development Administration, while accession SS_4 was obtained from Seoul Seed Company in Korea. Controlled crosses were made in the greenhouse in 1998 between the different parents and F1 hybrids to generate F2 and backcross generations. To study the inheritance of light green-yellow flower color, parents F1, F2 and backcross generations were grown in 21 cm pots in a protected vinyl-house in 1999. Petal color determinations were made using a Chroma Meter (Minolta, CR-200) in the morning hours from 9-12 am. Each plant was examined 4-5 times over a five day period and classified as having yellow or light green flower color. Standard color ratings from Chroma Meter were classified with color index ‘a’ as: light green < – 10.0, yellow > -10.0.
Results
The results of the inheritance study are shown in Table 1. All F1 hybrid plants resulting from the SS4 x Kw 695 and Dalgona x Kw 695 crosses produced yellow flowers. The resulting F2 populations of these crosses segregated in a 3 yellow : 1 light green ratio. Backcross plants of F1x SS 4 and F 1 x Dalgona produced yellow flowers. These same results were obtained both years and indicate that inheritance of the light green flower character in Kw 695 is governed by a single recessive gene. While the inheritance of fruit flesh and skin color (2,5), delayed green leaf color (3), yellow leaf color of older leaves and mature fruit and yellow leaf (1,6) have been published earlier, the inheritance of light green flower color was never reported. We propose the gf gene symbol for the light green flower trait.
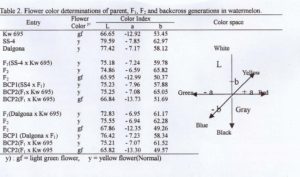
Measurement of watermelon flower color with a Chroma Meter allowed for accurate identification and classification. Watermelon flower color is commonly controlled by three factors: L, a, and b (Table 2). On the average, light green flowers showed ‘a’ values < -12.0, while yellow flower color values were > -8.0. Light green flowers never showed ‘a’ < -10.0 Therefore, this study indicates that a Chroma Meter can be used for accurate flower color determinations for this trait in watermelon.
Kw-695 plants have large vines with large, light green leaves. The plants produce large oval fruit of bright yellow green color with irregular dark green stripes, bright yellow-orange, inedible flesh with very low sugar content (about 3.2-0 Brix), and light yellow seeds. We think that the trait could be useful as a marker to identify lines or commercial cultivars in watermelon breeding programs. Linkages between this trait and other genetic characters in watermelon will be investigated.
Table 1. Segregation of light green flower and yellow color in parent, F1,F2, backcross generations on watermelon.
| Entry | No. of Tested Plant | Flower color | Expected ratio | X²value | P | |
| Yellow | Light green | |||||
| 1998 year | ||||||
|
15 | 0 | 15 | |||
|
14 | 14 | 0 | |||
|
15 | 15 | 0 | |||
|
10 | 10 | 0 | |||
|
33 | 21 | 12 | 3.1 | 2.276 | 0.5-0.1 |
|
22 | 22 | 0 | 1:0 | 0.059 | 0.9-0.5 |
|
17 | 9 | 8 | 1:1 | ||
|
12 | 12 | 0 | 1:0 | ||
|
37 | 32 | 5 | 3:1 | 2.604 | 0.5-0.1 |
| 1999 year | ||||||
|
14 | 0 | 14 | |||
|
13 | 13 | 0 | |||
|
13 | 13 | 0 | |||
|
5 | 5 | 0 | 1:0 | ||
|
81 | 81 | 25 | 3:1 | 1.458 | 0.5-0.1 |
|
13 | 13 | 0 | 1:0 | ||
|
47 | 47 | 19 | 1:1 | 1.723 | 0.5-0.1 |
|
5 | 5 | 0 | 1:0 | ||
|
69 | 69 | 16 | 3:1 | 0.120 | 0.9-0.5 |
|
12 | 12 | 0 | 1:0 | ||
|
32 | 32 | 14 | 1:1 | 0.500 | 0.5-0.1 |
Table 2. Flower color determinations of parent, F1, F2 and backcross generations in watermelon.
| Color Index | ||||||||||
| Entry | Flower Colory) | L | a | b | Color space | |||||
| KW 695 | gf | 66.65 | -12.92 | 53.45 | ||||||
| SS-4 | y | 79.59 | -7.85 | 62.97 | ||||||
| Dalgona | y | 77.42 | -7.17 | 58.12 | White | |||||
| F1(SS-4 x Kw695) | y | 75.18 | -7.24 | 59.78 | L | |||||
| F2 | y | 74.86 | -6.59 | 65.82 | ||||||
| F2 | gf | 65.95 | -12.99 | 50.37 | Yellow | |||||
| BCP1(SS4 x F1) | y | 75.23 | -7.96 | 57.88 | -b | |||||
| BCP2(F1 x Kw 695) | y | 75.25 | -7.08 | 65.05 | Green | -a | +a | Red | ||
| BCP2(F1 x Kw 695) | gf | 66.84 | -13.73 | 51.69 | ||||||
| F1(Dalgona x Kw 695) | y | 72.83 | -6.95 | 61.17 | ||||||
| F2 | y | 75.55 | -6.94 | 62.28 | -b | Gray | ||||
| F2 | gf | 67.86 | -12.35 | 49.26 | Blue | |||||
| BCP1 (Dalgona x F1) | y | 76.42 | -7.23 | 58.34 | ||||||
| BCP2(F1 x Kw 695 | y | 75.21 | -7.07 | 61.52 | Black | |||||
| BCP2(F1 x Kw 695 | gf | 65.82 | -13.30 | 49.57 | ||||||
y) : gf = light green flower, y = yellow flower (Normal)
Literature Cited
- Barham., W.S. 1956. A study of the Royal Golden watermelon with emphasis on the inheritance of the chlorotic condition characteristic of this variety. Proc. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci.. 67:487-489
- Mohr, H.C. 1986. Watermelon breeding. In: Bassett, M.J. (ed.) 1986. Breeding Vegetable Crops. AVI Publishing Co., Inc. p. 37-66.
- Rhodes, B.B. 1986. Genes affecting foliage color in watermelon. J. Hered. 77:134-135
- Rhodes, B.B. 1995. Gene list for watermelon (Citrullus lanatus). Cucurbit Genet. Coop. Rpt. 18:69-84.
- Shimotsuma, M. 1963. Cytogenetical studies in the genus Citrullus, VII. Inheritance of several characters in watermelon. Jape. J. Breeding 13:31-36.
- Wa rid, A. and A. A. Abide. 1976.Inheritance of marker genes of leaf color and ovary shape in watermelon, Citrullus lanatus Chad. Libyan J. Sci. 6A: 1-8.
- Weetman, L.M. 1957. Inheritance and correlation of shape, size and color in watermelon, C. vulgaris Schrad. Iowa Agric. Exp. Sta. Res. Bull. 228:221-256.