Cucurbit Genetics Cooperative Report 16:70-72 (article 25) 1993
Paulo T. Della Vecchia, Petro Terenciano S. and A,adeu Terenciano
Agroflora S/A, Caixa Postal 427, 12900-000 Braganca Paulista-SP, Brazil
Immature fruits of C. pepo and C. moschata are used in Brazil for raw or steamed salads. the market preference is towards C. pepo cultivars which bear slightly tapered, cylindrical fruits. However, the available C. pepo cultivars in Brazil are very susceptible to Papaya Ring Spot Virus-W which makes difficult their production, particularly during the late Spring and Summer periods. Some cultivars of C. moschata show good field resistance to PRSV-W, but they are late, produce plants with long vines and fruits that resemble the straightneck Butternut types. The present paper relates to the development of novel types of C. moschata with bush grown habit, good PRSV-W field resistance, earliness and which produce slightly tapered cylindrical fruits, similar to those of C. pepo.
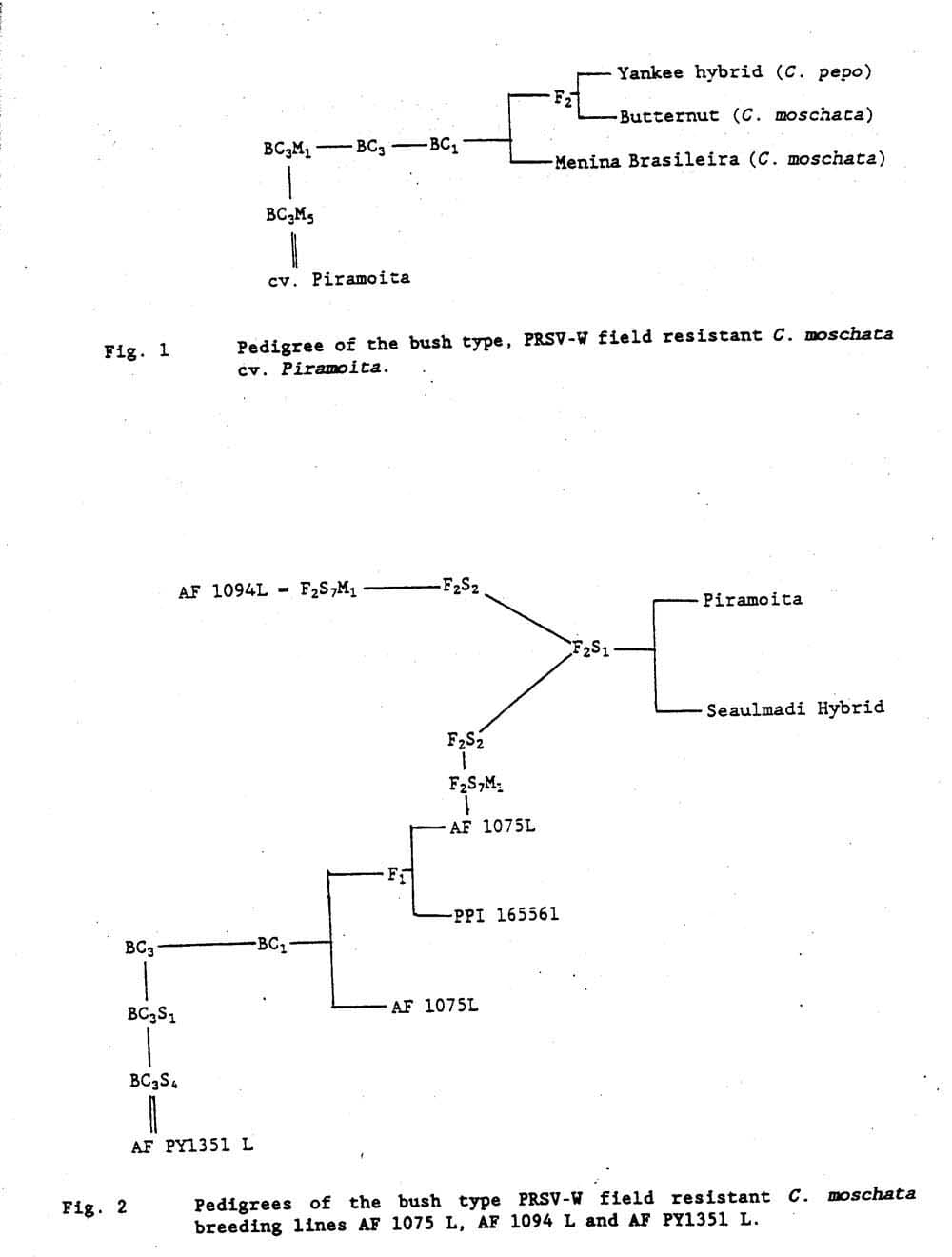
Method. The ines were obtained through pedigree and backcross selection as shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2. Selections for field resistance to PRSV-W were practiced in all generations, under natural field infection conditions, using spread rows and plants of C. pepo cv. Caserta as a standard immature squash type. Cv. Piramoita contributed the bush growth habit and PRSV-W resistance (1,2), F1 hybrid Seaulmadi the slightly tapered cylindrical fruit shape and PPI 165561 the precocious yellow fruit color (3).
Results. The main characteristics of the novel C. moschata breeding lines developed by the program are presented in Table 1.
Conclusions. Preliminary commercial field trials have indicated a good acceptance of the novel breeding lines among farmers in main production areas of Brazil. We believe that these novel types of C. moschata will be interesting to other tropical countries besides Brazil.
Table 1. Characteristics of some C. moschata breeding lines with bush growth habit and PRSV-W field resistance.
Characteristics |
Breeding Lines/Cultivar |
|||
AF1075 L |
AF1094 L |
AF1351 L |
Piramoita |
|
| Plant diameter (m) | 1,50 | 1,20 | 1,50 | 1.80 |
| Days for flowering | 55 | 50 | 55 | 55 |
| Sex of the 1st flower | female | male | female | female |
| Fruit length/diameter (cm) | 15/7 | 15/5 | 15/7 | — |
| Fruit colour | mottled light and dark green | uniform dark green | precocious yellow | mottled light and dark green |
| Fruit shape | tapered cylindr. | tapered cylindr | tapered cylindr. | long straightneck |
| Fruit growth1 (days) | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 |
| Productivity2 (fruits/plant) | 20-30 | 20-30 | 20-30 | 15-20 |
¹ Fruit growth – days from anthesis to the commercial harvesting size.
² Productivity – fruit/plant for a 40 days harvest period.
Figure 2. Pedigrees of the bush type PRSV-W field resistant C. moschata breeding lines AF 1075 L, AF 1094 L and AF PY1351 L.
Literature Cited
- Costa, C.P. da 1974. Obtencao de aborinha (Cucurbita moschata Duch ex Poir) Menina Brasileira com habito de crescimento tipo moita e com tolerancia ao Mosaico da Melancia. Revista de Olericultura XIV: 21-22.
- Munger, H,M, 1990. Availability and use of interspecific populations involving Cucurbita moschata and C. pepo. Cucurbit Genetics Coop. 13:49.
- Paris, H.S., Nerson, H. and Burger, Y. 1985. Precocious PI 165561, and Precocious PI 165561 R pumpkin breeding lines. Hort Science 20 (4): 778-779.